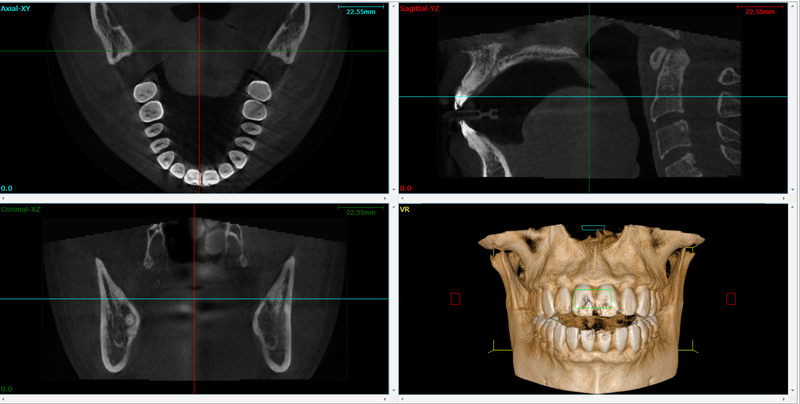
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), alternatively referred to as C-arm CT, flat-panel CT, or cone beam volume CT, utilizes divergent X-rays to generate a cone-shaped beam, offering a distinct medical imaging method beyond conventional X-rays.
CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) provides detailed 3D images of teeth and surrounding structures, aiding in precise diagnosis and treatment planning for root canals.
It's recommended for complex cases or when traditional X-rays don't provide enough information, like extensive decay or abnormal anatomy.
With high-resolution 3D images, CBCT exposes hidden canals, fractures, or calcifications, ensuring accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Though it exposes patients to slightly more radiation, the benefits usually outweigh the risks, given the enhanced treatment precision it offers.
Yes, by providing comprehensive insights beforehand, CBCT minimizes surprises during treatment, leading to improved success rates and fewer complications.

CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) provides detailed 3D images of teeth and surrounding structures, aiding in precise diagnosis and treatment planning for root canals.
It's recommended for complex cases or when traditional X-rays don't provide enough information, like extensive decay or abnormal anatomy.
With high-resolution 3D images, CBCT exposes hidden canals, fractures, or calcifications, ensuring accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Though it exposes patients to slightly more radiation, the benefits usually outweigh the risks, given the enhanced treatment precision it offers.
Yes, by providing comprehensive insights beforehand, CBCT minimizes surprises during treatment, leading to improved success rates and fewer complications.
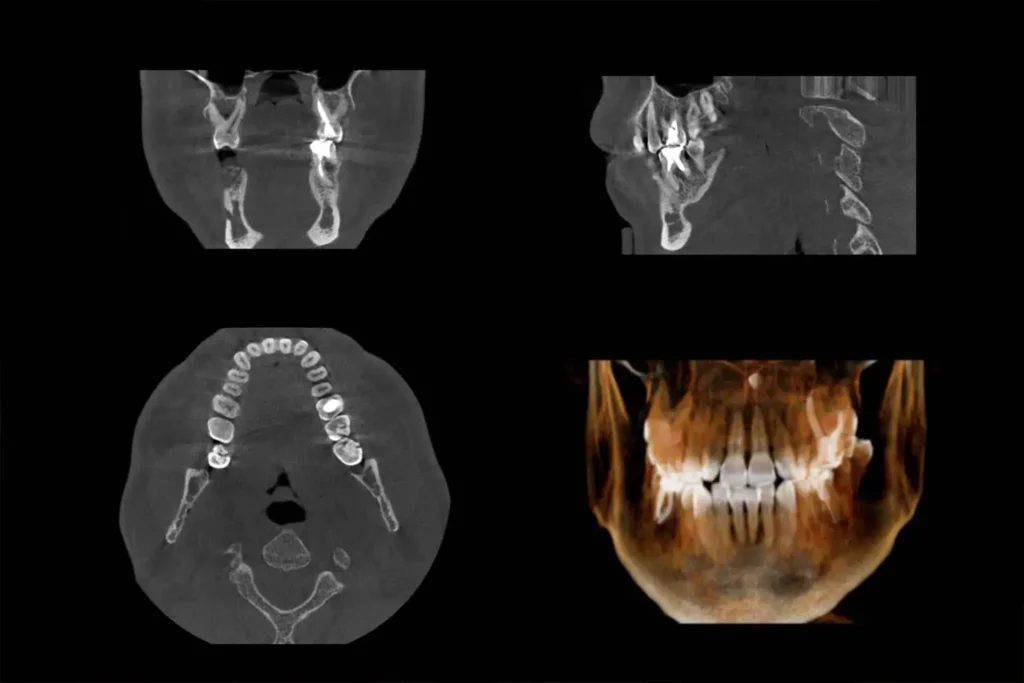
There are several key differences between CBCT and x-rays. One is that a CBCT is capable of showing soft tissue, in addition to bone, in the same image. Also, it shows both in greater detail than x-rays are able to provide of just bone. Finally, a CBCT, as opposed to x-rays, only leaves the most minimal amount of radiation behind.
CBCT in endodontics offers a major advantage: 3D imaging. This enhances evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment, akin to a medical CT scan. It detects cracks, unusual anatomy, and diseases with greater detail and efficiency than traditional CT scans, requiring just one rotation around the patient’s head.
The process begins with the patient undergoing a CBCT scan, which provides detailed 3D images of the tooth and surrounding structures. This step allows the dentist to accurately assess the root canal anatomy and identify any issues that need to be addressed.
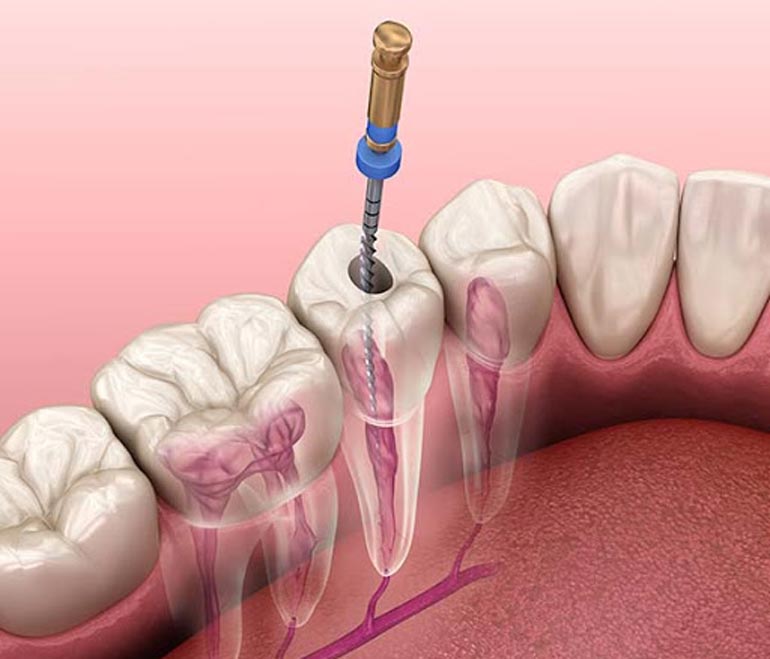
Once the diagnosis is complete, the dentist administers local anesthesia to numb the area before accessing the infected or damaged pulp inside the tooth. Using specialized instruments, the dentist carefully removes the infected tissue, cleans and shapes the root canals, and fills them with a biocompatible material to seal the tooth.

After the root canal procedure, the dentist may recommend a follow-up appointment to monitor the healing process. Depending on the extent of damage to the tooth, a final restoration, such as a filling or crown, may be placed to restore its function and appearance.




